Optimistic theory of history.
Human societies move towards higher and higher forms of culture or organization.
There is much disagreement as to the character of this improvement, as there is also much skepticismabout it.
Source:
David Miller et al., eds, The Blackwell Encyclopaedia of Political Thought (Oxford, 1987)
Measuring progress
Specific indicators for measuring progress can range from economic data, technical innovations, change in the political or legal system, and questions bearing on individual life chances, such as life expectancy and risk of disease and disability.
GDP growth has become a key orientation for politics and is often taken as a key figure to evaluate a politician’s performance. However, GDP has a number of flaws that make it a bad measure of progress, especially for developed countries. For example, environmental damage is not taken into account nor is the sustainability of economic activity. Wikiprogress has been set up to share information on evaluating societal progress. It aims to facilitate the exchange of ideas, initiatives and knowledge. HumanProgress.org is another online resource that seeks to compile data on different measures of societal progress.
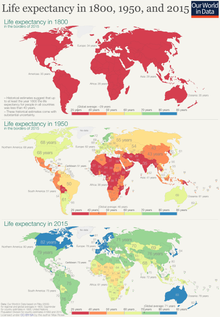
Life expectancy in 1800, 1950, and 2015 – visualization by Our World in Data
Our World in Data is a scientific online publication, based at the University of Oxford, that studies how to make progress against large global problems such as poverty, disease, hunger, climate change, war, existential risks, and inequality.[5] The mission of Our World in Data is to present “research and data to make progress against the world’s largest problems”.[6]
The Social Progress Index is a tool developed by the International Organization Imperative Social Progress, which measures the extent to which countries cover social and environmental needs of its citizenry. There are fifty-two indicators in three areas or dimensions: Basic Human Needs, and Foundations of Wellbeing and Opportunities which show the relative performance of nations.
Indices that can be used to measure progress include:
- Broad measures of economic progress
- Disability-adjusted life year
- Green national product
- Gender-related Development Index
- Genuine Progress Indicator
- Gross National Happiness
- Gross National Well-being
- Happy Planet Index
- Human Development Index
- Legatum Prosperity Index
- Social Progress Index
- OECD Better Life Index
- Subjective life satisfaction
- Where-to-be-born Index
- Wikiprogress
- World Happiness Report
- World Values Survey
Scientific progress
Scientific progress is the idea that the scientific community learns more over time, which causes a body of scientific knowledge to accumulate.[7] The chemists in the 19th century knew less about chemistry than the chemists in the 20th century, and they in turn knew less than the chemists in the 21st century. Looking forward, today’s chemists reasonably expect that chemists in future centuries will know more than they do.[7]
This process differs from non-science fields, such as human languages or history: the people who spoke a now-extinct language, or who lived through a historical time period, can be said to have known different things from the scholars who studied it later, but they cannot be said to know less about their lives than the modern scholars.[7] Some valid knowledge is lost through the passage of time, and other knowledge is gained, with the result that the non-science fields do not make scientific progress towards understanding their subject areas.[7]
From the 18th century through late 20th century, the history of science, especially of the physical and biological sciences, was often presented as a progressive accumulation of knowledge, in which true theories replaced false beliefs.[8] Some more recent historical interpretations, such as those of Thomas Kuhn, tend to portray the history of science in terms of competing paradigms or conceptual systems in a wider matrix of intellectual, cultural, economic and political trends. These interpretations, however, have met with opposition for they also portray the history of science as an incoherent system of incommensurable paradigms, not leading to any scientific progress, but only to the illusion of progress.[9]
Social progress
|
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (July 2018)
|
Aspects of social progress, as described by Condorcet, have included the disappearance of slavery, the rise of literacy, the lessening of inequalities between the sexes, reforms of harsh prisons and the decline of poverty.[10] The social progress of a society can be measured based on factors such as its ability to address fundamental human needs, help citizens improve their quality of life, and provide opportunities for citizens to succeed.[11]
Social progress is often improved by increases in GDP, although other factors are also relevant. An imbalance between economic and social progress hinders further economic progress, and can lead to political instability.[11]
Status of women
How progress improved the status of women in traditional society was a major theme of historians starting in the Enlightenment and continuing to today.[12] British theorists William Robertson (1721–1793) and Edmund Burke (1729–1797), along with many of their contemporaries, remained committed to Christian- and republican-based conceptions of virtue, while working within a new Enlightenment paradigm. The political agenda related beauty, taste, and morality to the imperatives and needs of modern societies of a high level of sophistication and differentiation. Two themes in the work of Robertson and Burke—the nature of women in ‘savage’ and ‘civilized’ societies and ‘beauty in distress’—reveals how long-held convictions about the character of women, especially with regard to their capacity and right to appear in the public domain, were modified and adjusted to the idea of progress and became central to modern European civilization.[13]
Classics experts have examined the status of women in the ancient world, concluding that in the Roman Empire, with its superior social organization, internal peace, and rule of law, allowed women to enjoy a somewhat better standing than in ancient Greece, where women were distinctly inferior.[14] The inferior status of women in traditional China has raised the issue of whether the idea of progress requires a thoroughgoing reject of traditionalism—a belief held by many Chinese reformers in the early 20th century.[15]
Historians Leo Marx and Bruce Mazlish asking, “Should we in fact abandon the idea of progress as a view of the past,” answer that there is no doubt “that the status of women has improved markedly” in cultures that have adopted the Enlightenment idea of progress.[16]
Modernization
Modernization was promoted by classical liberals in the 19th and 20th centuries, who called for the rapid modernization of the economy and society to remove the traditional hindrances to free markets and free movements of people.[17] During the Enlightenment in Europe social commentators and philosophers began to realize that people themselves could change society and change their way of life. Instead of being made completely by gods, there was increasing room for the idea that people themselves made their own society—and not only that, as Giambattista Vico argued, because people made their own society, they could also fully comprehend it. This gave rise to new sciences, or proto-sciences, which claimed to provide new scientific knowledge about what society was like, and how one may change it for the better.[18]
In turn, this gave rise to progressive opinion, in contrast with conservational opinion. The social conservationists were skeptical about panaceas for social ills. According to conservatives, attempts to radically remake society normally make things worse. Edmund Burke was the leading exponent of this, although later-day liberals like Hayek have espoused similar views. They argue that society changes organically and naturally, and that grand plans for the remaking of society, like the French Revolution, National Socialism and Communism hurt society by removing the traditional constraints on the exercise of power.
The scientific advances of the 16th and 17th centuries provided a basis for Francis Bacon’s book the New Atlantis. In the 17th century, Bernard le Bovier de Fontenelle described progress with respect to arts and the sciences, saying that each age has the advantage of not having to rediscover what was accomplished in preceding ages. The epistemology of John Locke provided further support and was popularized by the Encyclopedists Diderot, Holbach, and Condorcet. Locke had a powerful influence on the American Founding Fathers.[19] The first complete statement of progress is that of Turgot, in his “A Philosophical Review of the Successive Advances of the Human Mind” (1750). For Turgot, progress covers not only the arts and sciences but, on their base, the whole of culture—manner, mores, institutions, legal codes, economy, and society. Condorcet predicted the disappearance of slavery, the rise of literacy, the lessening of inequalities between the sexes, reforms of harsh prisons and the decline of poverty.[10]
John Stuart Mill’s (1806–1873) ethical and political thought demonstrated faith in the power of ideas and of intellectual education for improving human nature or behavior. For those who do not share this faith the idea of progress becomes questionable.[20]
Alfred Marshall (1842–1924), a British economist of the early 20th century, was a proponent of classical liberalism. In his highly influential Principles of Economics (1890), he was deeply interested in human progress and in what is now called sustainable development. For Marshall, the importance of wealth lay in its ability to promote the physical, mental, and moral health of the general population.[21] After World War II, the modernization and development programs undertaken in the Third World were typically based on the idea of progress.[22]
In Russia the notion of progress was first imported from the West by Peter the Great (1672–1725). An absolute ruler, he used the concept to modernize Russia and to legitimize his monarchy (unlike its usage in Western Europe, where it was primarily associated with political opposition). By the early 19th century, the notion of progress was being taken up by Russian intellectuals and was no longer accepted as legitimate by the tsars. Four schools of thought on progress emerged in 19th-century Russia: conservative (reactionary), religious, liberal, and socialist—the latter winning out in the form of Bolshevist materialism.[23]
The intellectual leaders of the American Revolution, such as Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Paine, Thomas Jefferson and John Adams, were immersed in Enlightenment thought and believed the idea of progress meant that they could reorganize the political system to the benefit of the human condition; both for Americans and also, as Jefferson put it, for an “Empire of Liberty” that would benefit all mankind.[24] In particular, Adams wrote “I must study politics and war, that our sons may have liberty to study mathematics and philosophy. Our sons ought to study mathematics and philosophy, geography, natural history and naval architecture, navigation, commerce and agriculture in order to give their children a right to study painting, poetry, music, architecture, statuary, tapestry and porcelain.”[citation needed]
Juan Bautista Alberdi (1810–1884) was one of the most influential political theorists in Argentina. Economic liberalism was the key to his idea of progress. He promoted faith in progress, while chiding fellow Latin Americans for blind copying of American and European models. He hoped for progress through promotion of immigration, education, and a moderate type of federalism and republicanism that might serve as a transition in Argentina to true democracy.[25]
In Mexico, José María Luis Mora (1794–1850) was a leader of classical liberalism in the first generation after independence, leading the battle against the conservative trinity of the army, the church, and the hacendados. He envisioned progress as both a process of human development by the search for philosophical truth and as the introduction of an era of material prosperity by technological advancement. His plan for Mexican reform demanded a republican government bolstered by widespread popular education free of clerical control, confiscation and sale of ecclesiastical lands as a means of redistributing income and clearing government debts, and effective control of a reduced military force by the government. Mora also demanded the establishment of legal equality between native Mexicans and foreign residents. His program, untried in his lifetime, became the key element in the Mexican Constitution of 1857.[26]
In Italy, the idea that progress in science and technology would lead to solutions for human ills was connected to the nationalism that united the country in 1860. The Piedmontese Prime Minister Camillo Cavour envisaged the railways as a major factor in the modernization and unification of the Italian peninsula. The new Kingdom of Italy, formed in 1861, worked to speed up the processes of modernization and industrialization that had begun in the north, but were slow to arrive in the Papal States and central Italy, and were nowhere in sight in the “Mezzogiorno” (that is, Southern Italy, Sicily, and Sardinia). The government sought to combat the backwardness of the poorer regions in the south and work towards augmenting the size and quality of the newly created Italian army so that it could compete on an equal footing with the powerful nations of Europe. In the same period, the government was legislating in favour of public education to fight the great problem of illiteracy, upgrade the teaching classes, improve existing schools, and procure the funds needed for social hygiene and care of the body as factors in the physical and moral regeneration of the race.[27]
In China, in the 20th century the Kuomintang or Nationalist party, which ruled from the 1920s to the 1940s, advocated progress. The Communists under Mao Zedong adopted western models and their ruinous projects caused mass famines. After Mao’s death, however, the new regime led by Deng Xiaoping (1904–1997) and his successors aggressively promoted modernization of the economy using capitalist models and imported western technology.[28] This was termed the “Opening of China” in the west, and more broadly encompasses Chinese economic reform.
Among environmentalists, there is a continuum between two opposing poles. The one pole is optimistic, progressive, and business-oriented, and endorses the classic idea of progress. For example, bright green environmentalism endorses the idea that new designs, social innovations and green technologies can solve critical environmental challenges. The other is pessimistic in respect of technological solutions,[29] warning of impending global crisis (through climate change or peak oil, for example) and tends to reject the very idea of modernity and the myth of progress that is so central to modernization thinking.[30] Similarly, Kirkpatrick Sale, wrote about progress as a myth benefiting the few, and a pending environmental doomsday for everyone.[31] An example is the philosophy of Deep Ecology

Well I truly enjoyed studying it. This information procured by you is very constructive for proper planning.
If you wish for to get much from this post then you have to apply such strategies to your won web site.|