A theory most familiarly associated with the English jurist Albert Venn Dicey (1835-1922).
People are governed by law rather than capriciously or arbitrarily, when all people including government and its officials are equally subject to law and when people are punishable only for an established breach of law.
Source:
David Miller et al., eds, The Blackwell Encyclopaedia of Political Thought (1987)
History
Although credit for popularizing the expression “the rule of law” in modern times is usually given to A. V. Dicey,[9][10] development of the legal concept can be traced through history to many ancient civilizations, including ancient Greece, Mesopotamia, India, and Rome.[11]
Antiquity
In the West, the ancient Greeks initially regarded the best form of government as rule by the best men.[12] Plato advocated a benevolent monarchy ruled by an idealized philosopher king, who was above the law.[12] Plato nevertheless hoped that the best men would be good at respecting established laws, explaining that “Where the law is subject to some other authority and has none of its own, the collapse of the state, in my view, is not far off; but if law is the master of the government and the government is its slave, then the situation is full of promise and men enjoy all the blessings that the gods shower on a state.”[13] More than Plato attempted to do, Aristotle flatly opposed letting the highest officials wield power beyond guarding and serving the laws.[12] In other words, Aristotle advocated the rule of law:
It is more proper that law should govern than any one of the citizens: upon the same principle, if it is advantageous to place the supreme power in some particular persons, they should be appointed to be only guardians, and the servants of the laws.[7]
The Roman statesman Cicero is often cited as saying, roughly: “We are all servants of the laws in order to be free.”[14] During the Roman Republic, controversial magistrates might be put on trial when their terms of office expired. Under the Roman Empire, the sovereign was personally immune (legibus solutus), but those with grievances could sue the treasury.[9]
In China, members of the school of legalism during the 3rd century BC argued for using law as a tool of governance, but they promoted “rule by law” as opposed to “rule of law”, meaning that they placed the aristocrats and emperor above the law.[15] In contrast, the Huang–Lao school of Daoism rejected legal positivism in favor of a natural law that even the ruler would be subject to.[16]
There has recently been an effort to reevaluate the influence of the Bible on Western constitutional law. In the Old Testament, the book of Deuteronomy imposes certain restrictions on the king, regarding such matters as the numbers of wives he might take and of horses he might acquire (for his own use). According to Professor Bernard M. Levinson, “This legislation was so utopian in its own time that it seems never to have been implemented….”[17] The Deuteronomic social vision may have influenced opponents of the divine right of kings, including Bishop John Ponet in sixteenth-century England.[18]
Middle Ages
In Islamic jurisprudence rule of law was formulated in the seventh century, so that no official could claim to be above the law, not even the caliph.[19]
Alfred the Great, Anglo-Saxon king in the 9th century, reformed the law of his kingdom and assembled a law code (the Doom Book) which he grounded on biblical commandments. He held that the same law had to be applied to all persons, whether rich or poor, friends or enemies. This was likely inspired by Leviticus 19:15: “You shall do no iniquity in judgment. You shall not favor the wretched and you shall not defer to the rich. In righteousness you are to judge your fellow.”[20]
In 1215, Archbishop Stephen Langton gathered the Barons in England and forced King John and future sovereigns and magistrates back under the rule of law, preserving ancient liberties by Magna Carta in return for exacting taxes.[21][22] This foundation for a constitution was carried into the United States Constitution.
In 1481, during the reign of Ferdinand II of Aragon, the Constitució de l’Observança was approved by the General Court of Catalonia, establishing the submission of royal power (included its officers) to the laws of the Principality of Catalonia.[23]
Early Modern Period
Amongst many other points of happiness and freedom which your majesty’s subjects of this kingdom have enjoyed under your royal progenitors, kings and queens of this realm, there is none which they have accounted more dear and precious than this, to be guided and governed by the certain rule of the law which giveth both to the head and members that which of right belongeth to them, and not by any uncertain or arbitrary form of government …[25]The first known use of this English phrase occurred around AD 1500.[24] Another early example of the phrase “rule of law” is found in a petition to James I of England in 1610, from the House of Commons:
In 1607, English Chief Justice Sir Edward Coke said in the Case of Prohibitions (according to his own report) “that the law was the golden met-wand and measure to try the causes of the subjects; and which protected His Majesty in safety and peace: with which the King was greatly offended, and said, that then he should be under the law, which was treason to affirm, as he said; to which I said, that Bracton saith, quod Rex non debet esse sub homine, sed sub Deo et lege (That the King ought not to be under any man but under God and the law.).”
Among the first modern authors to use the term and give the principle theoretical foundations was Samuel Rutherford in Lex, Rex (1644).[6] The title, Latin for “the law is king”, subverts the traditional formulation rex lex (“the king is law”).[26] James Harrington wrote in Oceana (1656), drawing principally on Aristotle’s Politics, that among forms of government an “Empire of Laws, and not of Men” was preferable to an “Empire of Men, and not of Laws”.[27]
John Locke also discussed this issue in his Second Treatise of Government (1690):
The natural liberty of man is to be free from any superior power on earth, and not to be under the will or legislative authority of man, but to have only the law of nature for his rule. The liberty of man, in society, is to be under no other legislative power, but that established, by consent, in the commonwealth; nor under the dominion of any will, or restraint of any law, but what that legislative shall enact, according to the trust put in it. Freedom then is not what Sir Robert Filmer tells us, Observations, A. 55. a liberty for every one to do what he lists, to live as he pleases, and not to be tied by any laws: but freedom of men under government is, to have a standing rule to live by, common to every one of that society, and made by the legislative power erected in it; a liberty to follow my own will in all things, where the rule prescribes not; and not to be subject to the inconstant, uncertain, unknown, arbitrary will of another man: as freedom of nature is, to be under no other restraint but the law of nature.[28]
The principle was also discussed by Montesquieu in The Spirit of the Laws (1748).[29] The phrase “rule of law” appears in Samuel Johnson’s Dictionary (1755).[30]
In 1776, the notion that no one is above the law was popular during the founding of the United States. For example, Thomas Paine wrote in his pamphlet Common Sense that “in America, the law is king. For as in absolute governments the King is law, so in free countries the law ought to be king; and there ought to be no other.”[31] In 1780, John Adams enshrined this principle in Article VI of the Declaration of Rights in the Constitution of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts:
No man, nor corporation, or association of men, have any other title to obtain advantages, or particular and exclusive privileges, distinct from those of the community, than what arises from the consideration of services rendered to the public; and this title being in nature neither hereditary, nor transmissible to children, or descendants, or relations by blood, the idea of a man born a magistrate, lawgiver, or judge, is absurd and unnatural.[32]
The influence of Britain, France and the United States contributed to spreading the principle of the rule of law to other countries around the world.[33][34]
Meaning and categorization of interpretations
The Oxford English Dictionary has defined rule of law this way:[2]
The authority and influence of law in society, esp. when viewed as a constraint on individual and institutional behaviour; (hence) the principle whereby all members of a society (including those in government) are considered equally subject to publicly disclosed legal codes and processes.
Rule of law implies that every citizen is subject to the law. It stands in contrast to the idea that the ruler is above the law, for example by divine right.
Despite wide use by politicians, judges and academics, the rule of law has been described as “an exceedingly elusive notion”.[35] Among modern legal theorists, one finds that at least two principal conceptions of the rule of law can be identified: a formalist or “thin” definition, and a substantive or “thick” definition; one occasionally encounters a third “functional” conception.[36] Formalist definitions of the rule of law do not make a judgment about the “justness” of law itself, but define specific procedural attributes that a legal framework must have in order to be in compliance with the rule of law. Substantive conceptions of the rule of law go beyond this and include certain substantive rights that are said to be based on, or derived from, the rule of law.[37]
Most legal theorists believe that the rule of law has purely formal characteristics. For instance, such theorists claim that law requires generality (general rules that apply to classes of persons and behaviors as opposed to individuals), publicity (no secret laws), prospective application (little or no retroactive laws), consistency (no contradictory laws),[38] equality (applied equally throughout all society), and certainty (certainty of application for a given situation), but formalists contend that there are no requirements with regard to the content of the law. Others, including a few legal theorists, believe that the rule of law necessarily entails protection of individual rights. Within legal theory, these two approaches to the rule of law are seen as the two basic alternatives, respectively labelled the formal and substantive approaches. Still, there are other views as well. Some believe that democracy is part of the rule of law.[39]
The “formal” interpretation is more widespread than the “substantive” interpretation. Formalists hold that the law must be prospective, well-known, and have characteristics of generality, equality, and certainty. Other than that, the formal view contains no requirements as to the content of the law.[36] This formal approach allows laws that protect democracy and individual rights, but recognizes the existence of “rule of law” in countries that do not necessarily have such laws protecting democracy or individual rights. The best known arguments for the formal interpretation have been made by A.V Dicey, F.A.Hayek, Joseph Raz, and Joseph Unger.
The substantive interpretation preferred by Dworkin, Laws, and Allan, holds that the rule of law intrinsically protects some or all individual rights.
The functional interpretation of the term “rule of law”, consistent with the traditional English meaning, contrasts the “rule of law” with the “rule of man”.[39] According to the functional view, a society in which government officers have a great deal of discretion has a low degree of “rule of law”, whereas a society in which government officers have little discretion has a high degree of “rule of law”.[39] Upholding the rule of law can sometimes require the punishment of those who commit offenses that are justifiable under natural law but not statutory law.[40] The rule of law is thus somewhat at odds with flexibility, even when flexibility may be preferable.[39]
The ancient concept of rule of law can be distinguished from rule by law, according to political science professor Li Shuguang: “The difference … is that, under the rule of law, the law is preeminent and can serve as a check against the abuse of power. Under rule by law, the law is a mere tool for a government, that suppresses in a legalistic fashion.”[41]
Status in various jurisdictions
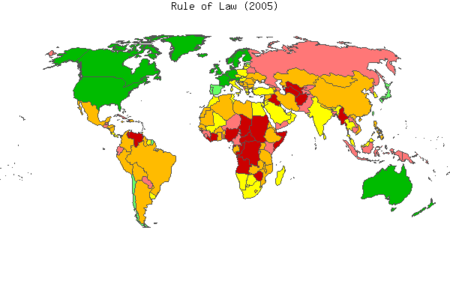
|
2005 map of Worldwide Governance Indicators, which attempts to measure the extent to which agents have confidence in and abide by the rules of society.
90–100th percentile*
75–90th percentile
50–75th percentile
25–50th percentile
10–25th percentile
0–10th percentile
* Percentile rank indicates the percentage of countries worldwide that rate below the selected country. |
The rule of law has been considered as one of the key dimensions that determine the quality and good governance of a country.[42] Research, like the Worldwide Governance Indicators, defines the rule of law as: “the extent to which agents have confidence and abide by the rules of society, and in particular the quality of contract enforcement, the police and the courts, as well as the likelihood of crime or violence.”[42] Based on this definition the Worldwide Governance Indicators project has developed aggregate measurements for the rule of law in more than 200 countries, as seen in the map at right.[43]
Europe
The preamble of the European Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms says “the governments of European countries which are like-minded and have a common heritage of political traditions, ideals, freedom and the rule of law”.
In France and Germany the concepts of rule of law (Etat de droit and Rechtsstaat respectively) are analogous to the principles of constitutional supremacy and protection of fundamental rights from public authorities (see public law), particularly the legislature.[44][45] France was one of the early pioneers of the ideas of the rule of law.[46] The German interpretation is more “rigid” but similar to that of France and the United Kingdom.[47][48]
Finland’s constitution explicitly requires rule of law by stipulating that “the exercise of public powers shall be based on an Act. In all public activity, the law shall be strictly observed.”
United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom the rule of law is a long-standing principle of the way the country is governed, dating from Magna Carta in 1215 and the Bill of Rights 1689.[26][49][50] In the 19th century, A. V. Dicey, a constitutional scholar and lawyer, wrote of the twin pillars of the British constitution in his classic work Introduction to the Study of the Law of the Constitution (1885); these two pillars are the rule of law and parliamentary sovereignty.[51]
Americas
United States
Scholars continue to debate whether the U.S. Constitution adopted a particular interpretation of the “rule of law”, and if so, which one. For example, John Harrison asserts that the word “law” in the Constitution is simply defined as that which is legally binding, rather than being “defined by formal or substantive criteria”, and therefore judges do not have discretion to decide that laws fail to satisfy such unwritten and vague criteria.[54] Law Professor Frederick Mark Gedicks disagrees, writing that Cicero, Augustine, Thomas Aquinas, and the framers of the U.S. Constitution believed that an unjust law was not really a law at all.[55]All government officers of the United States, including the President, the Justices of the Supreme Court, state judges and legislators, and all members of Congress, pledge first and foremost to uphold the Constitution. These oaths affirm that the rule of law is superior to the rule of any human leader.[52] At the same time, the federal government has considerable discretion: the legislative branch is free to decide what statutes it will write, as long as it stays within its enumerated powers and respects the constitutionally protected rights of individuals. Likewise, the judicial branch has a degree of judicial discretion,[53] and the executive branch also has various discretionary powers including prosecutorial discretion.
Some modern scholars contend that the rule of law has been corroded during the past century by the instrumental view of law promoted by legal realists such as Oliver Wendell Holmes and Roscoe Pound. For example, Brian Tamanaha asserts: “The rule of law is a centuries-old ideal, but the notion that law is a means to an end became entrenched only in the course of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries.”[56]
Others argue that the rule of law has survived but was transformed to allow for the exercise of discretion by administrators. For much of American history, the dominant notion of the rule of law, in this setting, has been some version of A. V. Dicey’s: “no man is punishable or can be lawfully made to suffer in body or goods except for a distinct breach of law established in the ordinary legal manner before the ordinary Courts of the land.” That is, individuals should be able to challenge an administrative order by bringing suit in a court of general jurisdiction. As the dockets of worker compensation commissions, public utility commissions and other agencies burgeoned, it soon became apparent that letting judges decide for themselves all the facts in a dispute (such as the extent of an injury in a worker’s compensation case) would overwhelm the courts and destroy the advantages of specialization that led to the creation of administrative agencies in the first place. Even Charles Evans Hughes, a Chief Justice of the United States, believed “you must have administration, and you must have administration by administrative officers.” By 1941, a compromise had emerged. If administrators adopted procedures that more or less tracked “the ordinary legal manner” of the courts, further review of the facts by “the ordinary Courts of the land” was unnecessary. That is, if you had your “day in commission”, the rule of law did not require a further “day in court”. Thus Dicey’s rule of law was recast into a purely procedural form.[57]
James Wilson said during the Philadelphia Convention in 1787 that, “Laws may be unjust, may be unwise, may be dangerous, may be destructive; and yet not be so unconstitutional as to justify the Judges in refusing to give them effect.” George Mason agreed that judges “could declare an unconstitutional law void. But with regard to every law, however unjust, oppressive or pernicious, which did not come plainly under this description, they would be under the necessity as judges to give it a free course.”[58] Chief Justice John Marshall (joined by Justice Joseph Story) took a similar position in 1827: “When its existence as law is denied, that existence cannot be proved by showing what are the qualities of a law.”[59]
Asia
East Asian cultures are influenced by two schools of thought, Confucianism, which advocated good governance as rule by leaders who are benevolent and virtuous, and Legalism, which advocated strict adherence to law. The influence of one school of thought over the other has varied throughout the centuries. One study indicates that throughout East Asia, only South Korea, Singapore, Japan, Taiwan and Hong Kong have societies that are robustly committed to a law-bound state.[60] According to Awzar Thi, a member of the Asian Human Rights Commission, the rule of law in Cambodia, and most of Asia is weak or nonexistent:
Apart from a number of states and territories, across the continent there is a huge gulf between the rule of law rhetoric and reality. In Thailand, the police force is favor over the rich and corrupted. In Cambodia, judges are proxies for the ruling political party … That a judge may harbor political prejudice or apply the law unevenly are the smallest worries for an ordinary criminal defendant in Asia. More likely ones are: Will the police fabricate the evidence? Will the prosecutor bother to show up? Will the judge fall asleep? Will I be poisoned in prison? Will my case be completed within a decade?[61]
In countries such as China and Vietnam, the transition to a market economy has been a major factor in a move toward the rule of law, because the rule of law is important to foreign investors and to economic development. It remains unclear whether the rule of law in countries like China and Vietnam will be limited to commercial matters or will spill into other areas as well, and if so whether that spillover will enhance prospects for related values such as democracy and human rights.[62] The rule of law in China has been widely discussed and debated by both legal scholars and politicians in China.
In Thailand, a kingdom that has had a constitution since the initial attempt to overthrow the absolute monarchy system in 1932, the rule of law has been more of a principle than actual practice.[citation needed] Ancient prejudices and political bias have been present in the three branches of government with each of their foundings, and justice has been processed formally according to the law but in fact more closely aligned with royalist principles that are still advocated in the 21st century.[citation needed] In November 2013, Thailand faced still further threats to the rule of law when the executive branch rejected a supreme court decision over how to select senators.[citation needed]
In India, the longest constitutional text in the history of the world has governed that country since 1950. Although the Constitution of India may have been intended to provide details that would limit the opportunity for judicial discretion, the more text there is in a constitution the greater opportunity the judiciary may have to exercise judicial review.[63] According to Indian journalist Harish Khare, “The rule of law or rather the Constitution [is] in danger of being supplanted by the rule of judges.”[64]
Japan had centuries of tradition prior to World War II, during which there were laws, but they did not provide a central organizing principle for society, and they did not constrain the powers of government (Boadi, 2001). As the 21st century began, the percentage of people who were lawyers and judges in Japan remained very low relative to western Europe and the United States, and legislation in Japan tended to be terse and general, leaving much discretion in the hands of bureaucrats

Very interesting information!Perfect just what I was looking for!
Excellent post. I used to be checking constantly this weblog and I’m impressed!
Very helpful information particularly the final section 🙂 I deal with such information much.
I used to be seeking this particular info for a long
time. Thank you and good luck.